Intro
A while ago, I was added as a curator for a Gem called JsonPath. It’s a small but very useful and brilliant gem. It had a couple of problems which I fixed, but the hardest to eliminate proved to be a series of evals throughout the code.
You could opt in using eval with a constructor parameter, but generally, it was considered to be unsafe. Thus, normally when a project was using it, like Huginn they had to opt out by default, thus missing out on sweet parsing like this: $..book[?(@['price'] > 20)].
Eval
In order to remove eval, first I had to understand what it is actually doing. I had to take it apart.
After much digging and understanding the code, I found, all it does is perform the given operations on the current node. And if the operation is true, it will select that node, otherwise, return false, and ignore that node.
For example $..book[?(@['price'] > 20)] could be translated to:
return @_current_node['price'] > 20
Checking first if 'price' is even a key in @_current_node. Once I’ve understood this part, I set on trying to fix eval.
SAFE = 4
In ruby, you could extract the part where you Eval and put it into its own proc and set SAFE = 4 which will disable some things like system calls.
proc do
SAFE = 4
eval(some_expression)
end.call
SAFE levels:
$SAFE Description 0 No checking of the use of externally supplied (tainted) data is performed. This is Ruby’s default mode.
= 1 Ruby disallows the use of tainted data by potentially dangerous operations. = 2 Ruby prohibits the loading of program files from globally writable locations. = 3 All newly created objects are considered tainted. = 4 Ruby effectively partitions the running program in two. None - tainted objects may not be modified. Typically, this will be used to create a sandbox: the program sets up an environment using a lower $SAFE level, then resets $SAFE to 4 to prevent subsequent changes to that environment.
This has the disadvantage that anything below 4 is just, meh. But nothing above 1 will actually work with JsonPath so… scratch that.
Sandboxing
We could technically try and sandbox eval into it’s own process with a PID and whitelist methods which are allowed to be called.
Not bad, and there are a few gems out there which are trying to do that like SafeRuby. But all of these project have been abandoned years ago for a good reason.
Object.send
Object.send is the best way to get some flexibility while still being safe. You basically just call methods on objects by describing said method on an object and giving parameters to it, like:
1.send(:+, 2) => 3
This is a very powerful tool in our toolbox which we will exploit immensely.
So let’s get to it.
Writing a parser
Writing a parser in Ruby is a very fluid experience. It has nice tools which support that, and the one I used is StringScanner. It has the ability to track where you are currently at in a string and move a pointer along with regex matches. In fact, JsonPath already employs this method when parsing a json expression. So reusing that logic was in fact… elementary.
The expression
How do we get from this:
$..book[?(@['price'] < 20)]
To this:
@_current_node['price'] < 20
Well. By simple elimination. There are a couple of problems along the way of course. Because this wouldn’t be a parser if it couldn’t handle ALL the other cases…
Removing Clutter
Some of this we don’t need. Like, $..book part.
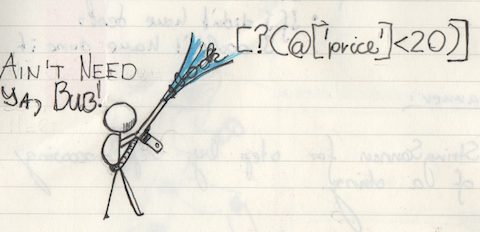
The other things we don’t need are all the '[]?()

Once this is done, we can move to isolating the important bits.
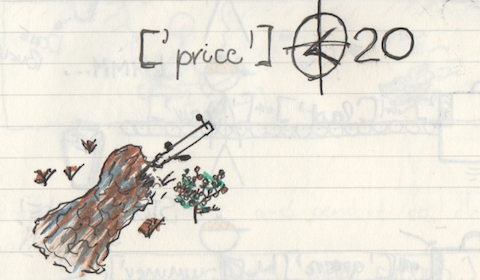
BreakDown
Elements
How does an expression actually look like?
Let’s break it down.
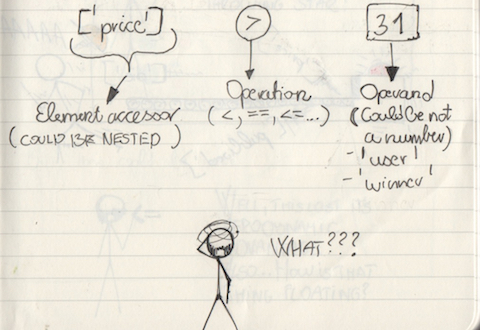
So, this is a handful. Operations can be <=,>=,<,>,==,!= and operands can be either numbers, or words, and element accessor can be nested since something like this is perfectly valid: $..book[?(@.written.year == 1997)].
To avoid being overwhelmed, ruby has our back with a method called dig.
This, basically lets us pass in some parameters into a dig function on a hash or an array with variadic parameters, which will go on and access those elements in order how they were supplied. Until it either returns a nil or an end result.
For example:
2.3.1 :001 > a = {a: {b: 'c'}}
=> {:a=>{:b=>"c"}}
2.3.1 :002 > a.dig(:a, :b)
=> "c"
Easy. However… Dig was only added after ruby 2.3 thus, I had to write my own dig for now, until I stop supporting anything below 2.3.
At first, I wanted to add it to the hash class, but it proved to be a futile attempt if I wanted to do it nicely, thus the parser got it as a private method.
def dig(keys, hash)
return hash unless hash.is_a? Hash
return nil unless hash.key?(keys.first)
return hash.fetch(keys.first) if keys.size == 1
prev = keys.shift
dig(keys, hash.fetch(prev))
end
And the corresponding regex behind getting a multitude of elements is as follows:
...
if t = scanner.scan(/\['\w+'\]+/)
...
Operator
Selecting the operator is another interesting part as it can be a single one or multiple and all sorts. Until I realized that no… it can actually be only a couple.


Also, after a bit of fiddling and doing and doing a silly case statement first:
case op
when '>'
dig(@_current_node, *elements) > operand
when '<'
dig(@_current_node, *elements) > operand
...
end
…I promptly saw that this is not how it should be done.
And here comes Object.send.

This gave me the opportunity to write this:
dig(elements, @_current_node).send(operator, operand)
Much better. Now I could send all the things in the way of a node.
Parsing an op be like:
elsif t = scanner.scan(/\s+[<>=][<>=]?\s+?/)
Operand
Now comes the final piece. The value which we are comparing. This could either be a simple integer, a floating number, or a word. Hah. So coming up with a regex which fits this tightly took a little fiddling, but eventually I ended up with this:
elsif t = scanner.scan(/(\s+)?'?(\w+)?[.,]?(\w+)?'?(\s+)?/)
Without StackOverflow I would say this is fine ((although I need to remove all those space check, shees)). What are all the question marks? Basically, everything is optional. Because an this expression $..book[?(@.price)] is valid. Which is basically just asserting if a given node has a price element.
Logical Operators
The last thing that remains is logical operators, which if you are using eval, is pretty straight forward. It takes care of anything that you might add in like &&, ||, |, &, ^ etc etc.
Now, that’s something I did with a case though. Until I find a nicer solution. Since we can already parse a single expression it’s just a question of breaking down a multi structure expression as the following one: $..book[?(@['price'] > 20 && @.written.year == 1998)].
exps = exp.split(/(&&)|(\|\|)/)
This splits up the string by either && or || and the usage of groups () also includes the operators. Than I evaluate the expressions and save the whole thing in an array like [true, '&&', false]. You know what could immediately resolve this? Yep…
 .
.
I’d rather just parse it although technically an eval at this stage wouldn’t be that big of a problem…
def parse(exp)
exps = exp.split(/(&&)|(\|\|)/)
ret = parse_exp(exps.shift)
exps.each_with_index do |item, index|
case item
when '&&'
ret &&= parse_exp(exps[index + 1])
when '||'
ret ||= parse_exp(exps[index + 1])
end
end
ret
end
Closing words
That’s it folks. The parser is done. And there is no eval being used. There are some more things here that are interesting. Like, array indexing is allowed in jsonpath which is solved by sending .length to a current node. For example:
if scanner.scan(/\./)
sym = scanner.scan(/\w+/)
op = scanner.scan(/./)
num = scanner.scan(/\d+/)
return @_current_node.send(sym.to_sym).send(op.to_sym, num.to_i)
end
If an expression begins with a .. So you see that using send will help a lot, and understanding what eval is trying to evaluate and rather writing your own parser, isn’t that hard at all using ruby.
I hope you enjoyed reading this little tid-bit as much as I enjoyed writing and drawing it. Leave a comment if your liked the drawings or if you did not and I should never do them again (( I don’t really care, this is my blog haha. )). Note to self: I shouldn’t draw on the other side of the drawing because of bleed-through.
Thank you! Gergely.